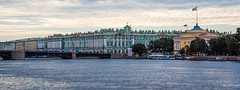Winter Palace
The Winter Palace (Russian: Зимний дворец) is a palace in Saint Petersburg that served as the official residence of the House of Romanov, previous emperors, from 1732 to 1917. The palace and its precincts now house the Hermitage Museum. Situated between Palace Embankment and Palace Square, adjacent to the site of Peter the Great's original Winter Palace, the present and fourth Winter Palace was built and altered almost continuously between the late 1730s and 1837, when it was severely damaged by fire and immediately rebuilt. The storming of the palace in 1917, as depicted in Soviet art and in Sergei Eisenstein's 1928 film October, became a symbol of the October Revolution.
The emperors constructed their palaces on a monumental scale that aimed to reflect the might and power of Imperial Russia. From the palace, the tsars ruled over (almost 1/6 of the Earth's landmass) and 125 million subjects by the end of the 19th century. Several architects participated in designing the Winter Palace—most notably the Italian Bartolomeo Rastrelli (1700–1771)—in what became known as the Elizabethan Baroque style. The green-and-white palace has the overall shape of an elongated rectangle, and its principal façade is long and high. The Winter Palace has been calculated to contain 1,886 doors, 1,945 windows, 1,500 rooms and 117 staircases. Following a serious fire, the palace's rebuilding of 1837 left the exterior unchanged, but large parts of the interior were redesigned in a variety of tastes and styles, leading the palace to be described as a "19th-century palace inspired by a model in Rococo style".
In 1905, the Bloody Sunday occurred when demonstrators marched toward the Winter Palace, but by this time the Imperial Family had chosen to live in the more secure and secluded Alexander Palace at Tsarskoe Selo (lit. "regal village"), and returned to the Winter Palace only for formal and state occasions. Following the February Revolution of 1917, the palace operated for a short time as the seat of the Russian Provisional Government, ultimately led by Alexander Kerensky. Later that same year a detachment of Red Guard soldiers and sailors stormed the palace—a defining moment in the birth of the Soviet state, overthrowing the Provisional Government.
Peter the Great's Winter Palace (1711–1753)
Upon returning from his Grand Embassy in 1698, Peter I of Russia embarked on a policy of Westernization and expansion that was to transform the Tsardom of Russia into the Russian Empire and a major European power. This policy was manifested in bricks and mortar by the creation of a new city, Saint Petersburg, in 1703. The culture and design of the new city was intended as a conscious rejection of traditional Byzantine-influenced Russian architecture, such as the then-fashionable Naryshkin Baroque, in favour of the classically inspired architecture prevailing in the great cities of Europe. The Tsar intended that his new city would be designed in a Flemish renaissance style, later known as Petrine Baroque, and this was the style he selected for his new palace in the city. The first Royal residence on the site had been a humble log cabin then known as the Domik Petra I, built in 1704, which faced the River Neva. In 1711 it was transported to the Petrovskaya Naberezhnaya, where it still stands. With the site cleared, the Tsar then embarked on the building of a larger house between 1711 and 1712. This house, today referred to as The First Winter Palace, was designed by Domenico Trezzini.
The 18th century was a period of great development in European royal architecture, as the need for a fortified residence gradually lessened. This process, which had begun in the late 16th century, accelerated and great classical palaces quickly replaced fortified castles throughout the more powerful European countries. One of the earliest and most notable examples was Louis XIV's Versailles. Largely completed by 1710, Versailles—with its size and splendour—heightened rivalry amongst the sovereigns of Europe. Peter the Great of Russia, keen to promote all western concepts, wished to have a modern palace like his fellow sovereigns. However, unlike some of his successors, Peter I never aspired to rival Versailles.
The first Winter Palace was a modest building of two main floors under a slate roof. It seems that Peter soon tired of the first palace, for in 1721 the second version of the Winter Palace was built under the direction of architect Georg Mattarnovy. Mattarnovy's palace, though still very modest compared to royal palaces in other European capitals, was on two floors above a rusticated ground floor, with a central projection underneath a pediment supported by columns. It was here that Peter the Great died in 1725.
The Winter Palace was not the only palace in the unfinished city, or even the most splendid, as Peter had ordered his nobles to construct stone built residences and to spend half the year there. This was an unpopular command; Saint Petersburg was founded upon a swamp, with little sunlight, and it was said only cabbages and turnips would grow there. It was forbidden to fell trees for fuel, so hot water was permitted just once a week. Only Peter's second wife, Empress Catherine, pretended to enjoy life in the new city.
As a result of pressed slave labour from all over the Empire, work on the city progressed quickly. It has been estimated that 200,000 people died in twenty years while building the city. A diplomat of the time, who described the city as "a heap of villages linked together, like some plantation in the West Indies", just a few years later called it "a wonder of the world, considering its magnificent palaces". Some of these new palaces in Peter's beloved Flemish Baroque style, such as the and the Menshikov Palace, still stand.
The palace, 1725–1855
On Peter the Great's death in 1725, the city of Saint Petersburg was still far from being the centre of western culture and civilization that he had envisioned. Many of the aristocrats who had been compelled by the Tsar to inhabit Saint Petersburg left. Wolves roamed the squares at night while bands of discontented pressed serfs, imported to build the Tsar's new city and Baltic fleet, frequently rebelled.
Peter I was succeeded by his widow, Catherine I, who reigned until her death in 1727. She in turn was succeeded by Peter I's grandson Peter II, who in 1727 had Mattarnovy's palace greatly enlarged by the architect Domenico Trezzini. Trezzini, who had designed the Summer Palace in 1711, was one of the greatest exponents of the Petrine Baroque style, now completely redesigned and expanded Mattarnovy's existing Winter Palace to such an extent that Mattarnovy's entire palace became merely one of the two terminating pavilions of the new, and third, Winter Palace. The third palace, like the second, was in the Petrine Baroque style.
In 1728, shortly after the third palace was completed, the Imperial Court left Saint Petersburg for Moscow, and the Winter Palace lost its status as the principal imperial residence. Moscow had once again been designated the capital city, a status which had been granted to Saint Petersburg in 1713. Following the death of Peter II in 1730 the throne passed to a niece of Peter I, Anna Ivanovna, Duchess of Courland.
Anna (1730–1740)
The new Empress cared more for Saint Petersburg than her immediate predecessors; she re-established the Imperial court at the Winter Palace, and in 1732 Saint Petersburg again officially replaced Moscow as Russia's capital, a position it was to hold until 1918.
Ignoring the third Winter Palace, the Empress on her return to Saint Petersburg took up residence at the neighbouring Apraksin Palace. In 1732, the Tsaritsa commissioned the Italian architect Francesco Bartolomeo Rastrelli to completely rebuild and extend the Apraksin Palace, incorporating other neighbouring houses. Thus, the core of the fourth and final Winter Palace is not the palace of Peter the Great, but the palace of Admiral General Fyodor Matveyevich Apraksin.
The Empress Anna, though unpopular and considered "dull, coarse, fat, harsh and spiteful", was keen to introduce a more civilized and cultured air to her court. She designed new liveries for her servants and, on her orders, mead and vodka were replaced with champagne and Burgundy. She instructed the Boyars to replace their plain furniture with that of mahogany and ebony, while her own tastes in interior decoration ran to a dressing table of solid gold and an "easing stool" of silver, studded with rubies. It was against such a backdrop of magnificence and extravagance that she gave her first ball in the newly completed gallery at the Winter Palace, which, in the middle of the Russian winter, resembled an orange grove. This, the fourth version of the Winter Palace, was to be an ongoing project for the architect Rastrelli throughout the reign of the Empress Anna.
Elizabeth (1741–1762)
The infant Tsar Ivan VI, succeeding Anna in 1740, was soon deposed in a bloodless coup d'état by Grand Duchess Elizabeth, a daughter of Peter the Great. The new Empress Elizabeth, whose main residence was the Summer Palace, led the court at the Winter Palace to be described later by the Russian historian Vasily Klyuchevsky as a place of "gilded squalor".
During the reign of Elizabeth, Rastrelli, still working to his original plan, devised an entirely new scheme in 1753, on a colossal scale—the present Winter Palace. The expedited completion of the palace became a matter of honour to the Empress, who regarded the palace as a symbol of national prestige. Work on the building continued throughout the year, even in the severest months of the winter. The deprivation to both the Russian people and the army caused by the ongoing Seven Years' War were not permitted to hinder the progress. 859,555 rubles had been allocated to the project, a sum raised by a tax on state-owned taverns. Though the labourers earned a monthly wage of just one ruble, the cost of the project exc…
Looking for places related to Winter Palace?
Those are other destinations to find places related to Winter Palace:
- Hermitage Museum
- Peter and Paul Fort…
- Winter
- Square
- Saint Michael's Cas…
- Constitutional Cour…
- Petrovsky Stadium
- Field of Mars
- Alexander Column
- Monument to Nichola…
- Cabin of Peter the …
- Mariinsky
- Marble
- Bronze Horseman
- Saint Peter's School
- The Passage
- Kokushkin Bridge
- Central Naval Museum
- Stroganov
- Tovstonogov Bolshoi…
- Imperial Academy of…
- Ciniselli Circus
- Eliseyev Emporium
- Apraksin Dvor